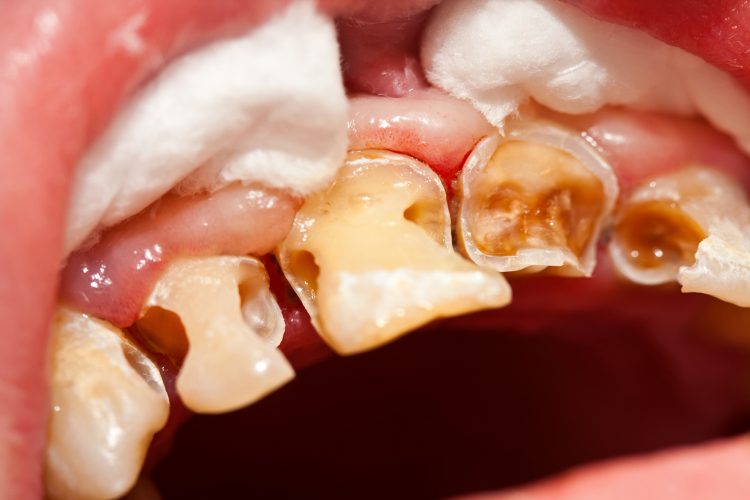
Dental caries, commonly known as “insect teeth” or “tooth decay”, is a chronic and progressive damage to the hard tissues of teeth caused by bacterial action. It not only affects aesthetics, but also leads to serious oral health problems, and even affects overall health. This article will delve into the causes, symptoms, prevention, and treatment methods of dental caries, helping readers gain a comprehensive understanding of this common but significant disease.
Cause analysis
The occurrence of dental caries is related to various factors, mainly including:
-Bacterial action: Certain bacteria in the oral cavity, such as streptococcus, can decompose food residues and produce acids that can erode the enamel on the surface of teeth, leading to mineral loss and the formation of cavities.
-Food residues: High sugar and high starch foods are prone to adhere to the surface of teeth, providing a breeding ground for bacterial growth.
-Saliva secretion: Saliva has the function of neutralizing acidity and cleaning food residues. Insufficient saliva secretion increases the risk of dental caries.
-Personal hygiene habits: Poor oral hygiene habits, such as irregular brushing and improper use of brushing tools, can increase the risk of dental caries.
– Genetic factors : Due to genetic reasons, some populations have fragile tooth structures and are more prone to dental caries.
Symptom manifestations
In the early stages of dental caries, there may be no obvious symptoms, but as the condition progresses, the following symptoms may appear:
-Surface discoloration of teeth: Initially manifested as white spots, gradually turning yellow brown or black.
– Tooth sensitivity : Sensitive to hot, cold, sweet, and sour stimuli, especially when eating hot and cold foods.
-Pain: When dental caries penetrate deep into the dentin layer, spontaneous pain or nighttime pain may occur.
-Dental pulp inflammation: In severe cases, it can cause dental pulp inflammation and even abscess, leading to severe pain.
Preventive measures
The key to preventing dental caries lies in good oral hygiene habits and a reasonable diet structure:
– Regular teeth cleaning : Thoroughly clean teeth, including gaps and posterior surfaces, at least twice a day.
– Use fluoride toothpaste : Fluoride helps enhance the acid resistance of teeth and reduce mineral loss.
– Reasonable diet : Reduce the intake of high sugar and high starch foods, eat more fiber rich foods such as vegetables and fruits to promote saliva secretion.
– Regular check ups : Conduct oral health check ups every six months to one year to promptly detect and treat early dental caries.
Treatment methods
The treatment methods vary depending on the degree of dental caries:
– Drug treatment : For initial caries, fluoride gel or mouthwash can be applied locally to promote remineralization.
– Filling treatment : When the cavity is deep, it is necessary to remove the decay and fill it with suitable materials (such as composite resin, silver amalgam) for repair.
-Root canal treatment: If the dental pulp is infected, root canal treatment is necessary to remove the infected tissue, fill the root canal, and finally restore the shape of the teeth.
– Tooth extraction : For severe dental caries that cannot be preserved, it may be necessary to remove them and consider subsequent restoration options such as dental implants or bridging.
In short, dental caries is a disease that can be effectively controlled through active prevention and timely treatment. Establishing good oral hygiene habits and conducting regular oral examinations are effective ways to prevent and detect dental caries at an early stage. Once any abnormalities are found in the teeth, it is important to seek medical attention promptly to prevent the condition from worsening and ensure oral health.












































Discussion about this post