Introduction
Dental erosion refers to an oral disease in which enamel and dentin are gradually lost due to the action of acidic substances. Acid corrosion not only affects the appearance of teeth, but may also lead to tooth sensitivity, pain, and functional impairment. This article will delve into the symptoms, causes, prevention, and treatment methods of dental erosion, helping readers to comprehensively understand and manage this issue and protect dental health.
Symptoms of dental erosion
The symptoms of dental erosion are diverse, and may not be obvious in the early stages, but as the condition progresses, the symptoms will gradually become apparent. Common symptoms include:
- Tooth sensitivity : When exposed to cold, hot, sweet, sour, or mechanical stimuli, teeth may experience brief and severe pain.
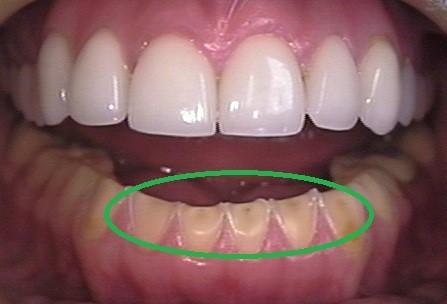
- Tooth discoloration: After the enamel wears down, the dentin is exposed, making the teeth appear more yellow or darker.
- Changes in tooth morphology: The surface of the teeth becomes rough or concave, and the tips of the teeth become dull or disappear.
- Increased tooth transparency : The enamel becomes thinner, and transparent areas appear on the surface of the teeth.
- Tooth fracture : Severe acid erosion may cause structural damage to teeth, resulting in cracks or fractures.
- Chewing difficulties : Changes in tooth morphology affect bite relationships, leading to difficulty chewing.
The causes of dental erosion
The causes of dental erosion are diverse, involving multiple aspects such as physiology, mechanics, and lifestyle habits
- Dietary factors :
Acidic foods and beverages: Frequent intake of acidic foods and beverages such as lemon juice, carbonated drinks, tomato sauce, etc. can cause enamel softening and wear.
High sugar diet: High sugar foods and beverages ferment in the mouth to produce acidic substances, accelerating the erosion of dental enamel. - Gastric acid reflux :
Gastroesophageal Reflux: Gastric acid refluxes into the mouth, causing dental erosion.
Vomiting: Frequent vomiting, such as pregnancy vomiting or binge eating disorder, can cause stomach acid to enter the mouth and erode tooth enamel. - Drug side effects :
Certain medications, such as antacids and drugs containing acidic components, may cause dental erosion. - Occupational exposure :
Industrial environment: In certain occupational environments, such as chemical plant workers, prolonged exposure to acidic substances may lead to dental erosion. - Poor oral hygiene:
Irregular brushing : Irregular brushing and flossing can lead to the accumulation of dental plaque and tartar, increasing the risk of erosion.
Improper brushing method: Using a hard bristled toothbrush or brushing too hard may cause gum damage and enamel wear. - Systemic diseases :
Insufficient saliva secretion: Saliva has the function of neutralizing acidity and cleaning teeth. Insufficient saliva secretion increases the risk of dental erosion.
Immune system diseases: People with weakened immune system function have an increased risk of developing dental erosion.
Preventive measures for dental erosion
The key to preventing dental erosion lies in improving lifestyle habits and maintaining good oral hygiene:
- Healthy diet :
Reduce acidic foods and beverages : Limit the intake of acidic foods and beverages such as lemon juice, carbonated drinks, tomato sauce, etc.
Increase alkaline foods : Consume alkaline rich foods such as vegetables, fruits, etc., to neutralize the acidic environment in the mouth.
Rinse mouth after meals: Rinse mouth with water or fluoride mouthwash after meals to reduce food residue and acidic substances. - Maintain good oral hygiene :
Correct brushing : Brush your teeth at least twice a day for at least two minutes each time, using a soft bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste.
Use dental floss : Use dental floss or interdental brushes daily to clean the gaps between teeth and remove dental plaque.
Mouthwash : Use antibacterial mouthwash to reduce the number of bacteria in the mouth and prevent plaque formation. - Avoid bad habits :
Quit smoking : Smoking is an important risk factor for tooth decay and should be quit as much as possible.
Avoid excessive brushing : Avoid using hard bristled toothbrushes or brushing excessively to prevent enamel wear.
Avoid biting hard objects : Do not bite hard objects with your teeth to avoid unnecessary damage. - Regular Inspection :
Dental examination: Conduct a comprehensive dental examination every six months to one year to promptly detect and treat early lesions.
Professional scaling : Regularly perform dental scaling to remove tartar and plaque, and prevent periodontal disease.
Treatment methods for dental erosion
Once dental erosion occurs, seek medical attention promptly and take appropriate treatment measures according to the condition:
- Drug therapy :
Fluoride containing gel or ointment : Use fluoride containing gel or ointment locally to help strengthen enamel and reduce sensitivity.
Antibiotics : Use oral or topical antibiotics under the guidance of a doctor to control infections. - Repair treatment :
Filling treatment: For teeth with acid erosion, composite resin or glass ionomer materials can be used for filling to restore the appearance and function of the teeth.
Dental crowns or veneers: For severely corroded teeth, dental crowns or veneers can be used for restoration to protect the surface of the teeth and reduce sensitivity. - Desensitization treatment :
Desensitizer : Dentists can use professional desensitizers in the clinic and apply them directly to sensitive areas to relieve pain.
Potassium salt preparation: Using toothpaste or mouthwash containing potassium nitrate or potassium chloride can seal dentinal tubules and alleviate sensitivity symptoms. - Physical therapy :
Laser therapy: Using lowintensity laser to promote the closure of dentinal tubules and alleviate sensitivity symptoms through the action of light energy.
Cold compress : Gently apply ice cubes or a cold towel to sensitive areas to relieve pain and swelling. - Surgical treatment :
Gum transplantation: For teeth sensitivity caused by gum recession, gum transplantation surgery can be performed to cover the exposed tooth roots and reduce sensitivity.
Bone transplantation: For severe alveolar bone resorption, bone transplantation surgery can be performed to restore bone mass and support teeth. - Psychological Intervention :
Counseling : For teeth sensitivity caused by psychological factors such as anxiety and tension, you can seek the help of a psychological counselor to learn how to cope with stress.
Conclusion
Dental erosion is a common oral problem that affects the appearance and function of teeth. By understanding the symptoms, causes, and prevention methods of dental erosion, we can take scientific and reasonable measures to effectively manage and prevent this problem. I hope this article can help readers better understand the prevention and treatment plans for dental erosion, take appropriate preventive and treatment measures, and protect their own and their family’s dental health. Through comprehensive management and timely treatment, we can resist the invasion of acidic foods and enjoy a healthy and comfortable oral life.












































Discussion about this post