Introduction
Gum disease, or periodontal disease, is one of the most common health conditions affecting adults worldwide. It starts with the accumulation of plaque—a sticky layer of bacteria—that gradually hardens into tartar if not removed regularly. Over time, this tartar leads to inflammation and infection of the gums. The condition, in its early stages, is known as gingivitis. Gingivitis is characterized by red, swollen gums that bleed easily during brushing or flossing. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress into a more severe form of gum disease called periodontitis, which can result in tooth loss and other serious oral health issues.
The good news is that gum disease, in its earliest stages, is reversible. By adopting proper dental care and seeking professional intervention, you can reverse gingivitis and restore your gums to a healthy state before the disease progresses. Understanding the signs of gum disease, knowing how to manage the condition at home, and seeking timely professional treatment are crucial to reversing the early stages of gum disease.
This article provides insights into identifying the early warning signs of gum disease, the importance of professional cleanings, and how daily oral hygiene practices such as brushing and flossing can play a significant role in reversing gingivitis.
Identifying the Early Signs of Gum Disease
Recognizing the early stages of gum disease is crucial in reversing the condition before it becomes more severe. The first signs of gum disease are often subtle, which is why many people overlook them. However, if you know what to look for, you can catch gum disease early and take action to stop it in its tracks.
1. Bleeding Gums
One of the most common and earliest signs of gum disease is bleeding gums, especially when brushing or flossing. Healthy gums should not bleed easily, so if you notice that your gums bleed during routine oral care, it could be a sign of gingivitis. While occasional bleeding can be normal for some people, frequent or persistent bleeding is an indication that something more serious might be developing.
2. Red or Swollen Gums
Healthy gums should have a pink hue and a firm texture. If your gums appear red or swollen, it may be due to the inflammation caused by an accumulation of plaque and bacteria. Swollen gums can also be tender and may feel sore when touched. This is a clear sign that gingivitis is present.
3. Bad Breath (Halitosis)
Persistent bad breath, or halitosis, is another sign of gum disease. The bacteria that build up on the gums and teeth in the early stages of gum disease can cause foul odors. While bad breath can be caused by other factors such as food or dry mouth, if it is accompanied by bleeding or swollen gums, it may be a sign of gingivitis.
4. Receding Gums
In the early stages of gum disease, the gums may begin to recede slightly from the teeth. This is a sign that the gums are being damaged by bacteria. Receding gums can expose the roots of the teeth, making them more sensitive and prone to decay.
5. Tenderness or Pain When Touching the Gums
If your gums feel sore when touched or if you experience tenderness while brushing, this can be an early indicator of gum disease. The discomfort is caused by the inflammation of the gums and the irritation from plaque buildup.
If you notice any of these symptoms, it is important to take action immediately to reverse the condition and avoid its progression into more severe stages. The sooner you start addressing the issue, the better the chances of a complete recovery.
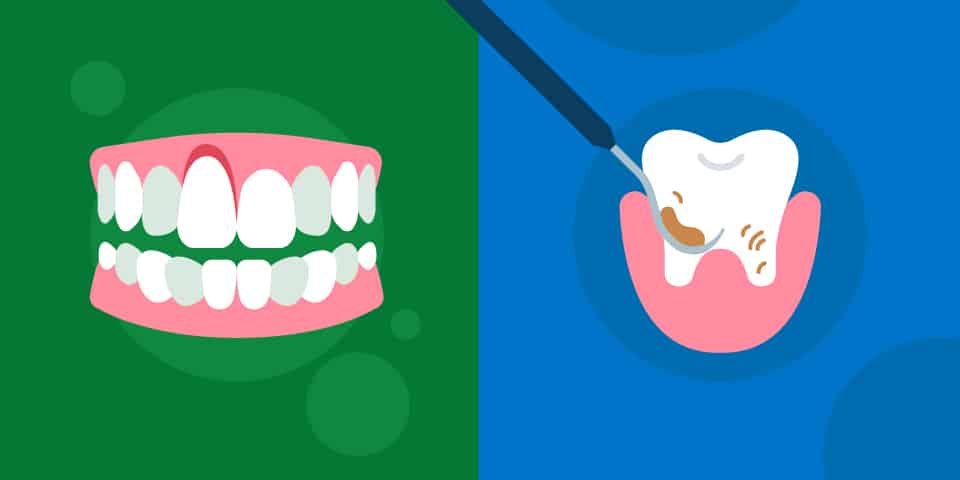

The Importance of Professional Cleanings
While daily oral hygiene plays a key role in preventing and reversing gum disease, professional cleanings by a dentist or dental hygienist are essential for removing tartar and plaque buildup that you cannot remove at home.
1. Why Regular Cleanings Matter
Plaque begins to harden into tartar after about 24 to 48 hours, and once tartar forms, it cannot be removed with a toothbrush or floss. This hardened plaque contributes to the inflammation of the gums and is a major factor in the development of gum disease. A professional cleaning involves the removal of both plaque and tartar from above and below the gumline, which is critical for restoring gum health.
2. Scaling and Root Planing
In cases of early gum disease, a dentist may recommend a deep cleaning procedure known as scaling and root planing. This procedure involves cleaning the tooth surfaces and the roots to remove tartar and bacteria that may have accumulated beneath the gumline. It also smooths the roots of the teeth, which helps the gums reattach more securely to the teeth. Scaling and root planing is typically the first line of treatment for gingivitis and can help reverse the condition.
3. Checking for Progression
During professional cleanings, your dentist or hygienist will evaluate the health of your gums and measure any pockets between your teeth and gums. These measurements help determine if gum disease is progressing. If pockets are shallow, the gum disease may still be reversible with good oral care at home. If the pockets are deeper, more intensive treatments may be necessary.
4. Regular Visits to Prevent Recurrence
Even after gum disease is reversed, regular dental visits are essential to prevent it from recurring. Routine cleanings every six months will help maintain gum health and detect any early signs of issues before they become major concerns. Regular check-ups also allow your dentist to monitor the health of your gums and ensure that any necessary treatments are provided promptly.
How At-Home Care (Brushing, Flossing) Plays a Role in Reversal
At-home care is perhaps the most important part of reversing early gum disease. While professional cleanings are vital, daily care plays a significant role in managing the condition and preventing it from progressing. Here are some essential practices that will help you keep your gums healthy and reverse the early stages of gum disease:
1. Brushing Your Teeth Correctly
Brushing your teeth at least twice a day is the foundation of good oral hygiene. Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste to gently clean your teeth and gums. Make sure to brush along the gumline, where plaque is most likely to build up. Be gentle, as aggressive brushing can irritate the gums and contribute to gum recession. Brushing correctly will remove plaque before it has the chance to turn into tartar.
2. Flossing Daily
Flossing is just as important as brushing for preventing gum disease. Flossing helps remove food particles and plaque from between your teeth and along the gumline—areas that a toothbrush may miss. If plaque is allowed to remain between the teeth, it can lead to gum inflammation. Make sure to floss gently to avoid irritating the gums.
3. Using Mouthwash
Mouthwash can be a helpful adjunct to brushing and flossing. Antiseptic mouthwashes can help reduce the bacteria in the mouth and promote healing of inflamed gums. Some mouthwashes contain fluoride, which can help strengthen tooth enamel and fight plaque. Be sure to choose a mouthwash that is alcohol-free, as alcohol-based mouthwashes can dry out the mouth and irritate the gums.
4. Avoiding Tobacco and Unhealthy Habits
Tobacco use is one of the leading risk factors for gum disease, so it is essential to avoid smoking or using smokeless tobacco. Tobacco impairs blood flow to the gums, which hinders the healing process. In addition to quitting tobacco, it’s important to maintain a healthy diet rich in vitamins and minerals that support gum health, such as vitamin C, calcium, and omega-3 fatty acids.
5. Drinking Plenty of Water
Water helps rinse away food particles and bacteria from the mouth, which can reduce plaque buildup. It also helps maintain the moisture in your mouth, which is crucial for gum health. Staying hydrated promotes the production of saliva, which naturally protects the gums and teeth from decay.
Conclusion
Reversing the early stages of gum disease is possible, and the key to success lies in early detection and proper care. By recognizing the early warning signs of gingivitis, seeking professional cleanings, and practicing good at-home oral hygiene habits such as brushing, flossing, and using mouthwash, you can restore your gum health and prevent the progression of gum disease. Remember, the sooner you take action, the better the chances of a full recovery. Don’t wait for the condition to worsen—act now to preserve your smile and protect your overall health.










































Discussion about this post