I. Introduction
Teeth whitening has always been a hot topic in cosmetic dentistry. With the improvement of living standards and an increasing awareness of aesthetics, more and more people are seeking ways to achieve a more confident and radiant smile. Traditional methods for teeth whitening, such as whitening toothpaste and teeth bleaching, may yield some results but typically require prolonged use. Cold light whitening, as a modern technology, has gradually become the preferred choice for teeth whitening due to its significant effects and relatively short treatment period.
Cold light teeth whitening (also known as cold light bleaching or laser whitening) is a technique that uses light to catalyze a chemical reaction, allowing a whitening agent to break down the colored substances on the tooth surface, thereby achieving teeth whitening. It has been widely applied in clinical dentistry, and with continuous technological advances, the effectiveness and safety of cold light whitening have improved significantly.
This article will explore in detail the principles, indications, advantages and limitations, procedure, effectiveness assessment, and future trends of cold light teeth whitening, helping readers gain a comprehensive understanding of this technique.
II. The Principles of Cold Light Teeth Whitening
The core principle of cold light whitening is the use of high-intensity blue light or other wavelengths of laser light in combination with specific whitening agents (such as hydrogen peroxide) to catalyze a chemical reaction that breaks down the colored substances on the tooth surface.
2.1 Basic Principle of Photochemical Reactions
Cold light whitening mainly involves exposing the whitening agent to blue light or laser light, which activates hydrogen peroxide molecules and releases free radicals. These free radicals react with organic pigments on the tooth surface, breaking them down into colorless substances, thus whitening the teeth.
2.2 Role of Whitening Agents
The whitening agents used in cold light whitening typically contain hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide. These compounds penetrate the enamel and dentin of the teeth, breaking down internal chromophores to achieve whitening. The light stimulates the whitening agent, speeding up the breakdown process and thus enhancing the whitening effect.
III. Indications for Cold Light Teeth Whitening
Cold light whitening is suitable for a variety of tooth discoloration problems caused by external or internal factors, including the following:
3.1 Extrinsic Staining
Extrinsic staining is caused by external pigments adhering to the tooth surface, such as coffee, tea, red wine, and smoking. Cold light whitening is highly effective in removing these stains, which typically accumulate on the outer layer of the enamel.
3.2 Intrinsic Staining
Intrinsic staining occurs when the inner structure of the tooth, such as dentin, becomes discolored. This type of discoloration is usually caused by medications (e.g., tetracycline), dental trauma, or aging. While cold light whitening can improve mild intrinsic stains, it may not be as effective for severe intrinsic discoloration.
3.3 Age-Related Discoloration
As people age, their teeth tend to become more yellow or dark. Cold light whitening can effectively address age-related discoloration, helping to restore the teeth to their natural whiteness.
3.4 Whitening Before Restorative Treatments
For patients planning dental restorations (such as veneers, crowns, etc.), cold light whitening can be performed beforehand to ensure that the color of the restorations matches the natural teeth.
IV. Advantages of Cold Light Teeth Whitening
4.1 Efficiency and Speed
One of the main advantages of cold light whitening is its efficiency and speed. Traditional whitening methods may require months of consistent use, while cold light whitening can achieve noticeable results in a single session, typically taking around 30 to 60 minutes.
4.2 High Safety
Compared to other whitening methods such as laser whitening, cold light whitening uses a gentler light source with lower temperatures, effectively preventing thermal damage to the teeth and gums. Additionally, because the light only activates the whitening agent, the surrounding tissues are minimally affected, making the treatment safer.
4.3 Aesthetic Results
Cold light whitening provides excellent aesthetic results, restoring a natural, bright white color to the teeth. It is more durable than traditional whitening treatments and helps reduce the recurrence of stains on the teeth.
4.4 Broad Applicability
Cold light whitening is not only effective for extrinsic stains, but it can also improve mild intrinsic staining. It is particularly effective in addressing age-related discoloration, tobacco stains, and coffee stains, making it a versatile option for a wide range of patients.
V. The Cold Light Teeth Whitening Procedure
The cold light whitening procedure is generally performed by a dentist and involves several steps. The process is relatively simple, and the patient’s comfort is usually well-maintained.
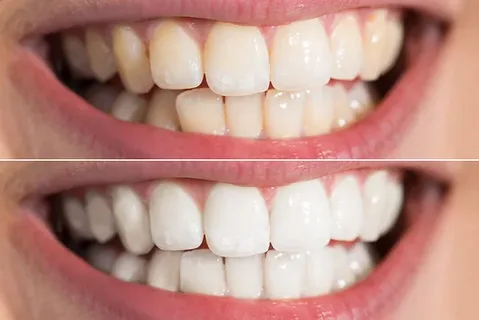
5.1 Pre-Treatment Evaluation
Before starting the cold light whitening procedure, the dentist will conduct a thorough oral examination, including X-rays and other diagnostic tests, to assess the condition of the teeth and gums, the cause of discoloration, and the expected whitening outcomes. If the patient has periodontal disease, cavities, or other oral health issues, they may need to be treated first.
5.2 Tooth Cleaning
Cleaning the teeth before whitening is crucial. The dentist will typically remove tartar, plaque, and other debris from the teeth to ensure that the whitening agent can be applied evenly to the surface.
5.3 Gum Protection
During the whitening treatment, the gums may be exposed to the whitening agent, so the dentist will typically apply a protective gel or use a special barrier to shield the gums from irritation or damage.
5.4 Application of Whitening Agent
The dentist will apply a whitening agent containing hydrogen peroxide or other whitening compounds evenly on the tooth surface. The concentration and type of whitening agent used depend on the degree of discoloration and the patient’s needs.
5.5 Light Exposure
Once the whitening agent is applied, the dentist will use a cold light source (typically blue LED light or laser) to activate the whitening agent. This light helps accelerate the breakdown of colored substances on the teeth.
5.6 Conclusion and Effect Evaluation
After the treatment, the dentist will assess the results and check for any remaining stains. Adjustments may be made if necessary. Typically, patients will notice significant whitening immediately after the treatment.
VI. Effectiveness Assessment of Cold Light Teeth Whitening
6.1 Immediate Results
The effects of cold light whitening are usually visible after just one treatment. Many patients report that their teeth appear noticeably whiter and brighter, and in some cases, the difference is quite striking.
6.2 Lasting Results
The results of cold light whitening are long-lasting but not permanent. Typically, patients need to avoid foods and beverages that can cause staining (such as coffee, red wine, and smoking) to maintain the whitening effect. The whitening effect generally lasts for one year or longer, depending on the individual’s habits and oral care.
6.3 Possible Side Effects
Although cold light whitening is generally safe, some patients may experience temporary tooth sensitivity or mild gum irritation. These symptoms usually resolve on their own within a short period after treatment. If discomfort persists, the patient should consult the dentist.
VII. Limitations and Precautions of Cold Light Teeth Whitening
7.1 Limited Effectiveness for Intrinsic Staining
Cold light whitening is highly effective for extrinsic staining (such as stains from smoking, coffee, etc.), but its effectiveness for intrinsic staining (such as discoloration caused by tetracycline or fluorosis) is limited. In such cases, alternative treatments, such as veneers or crowns, may be more appropriate.
7.2 Tooth Sensitivity
Some patients may experience short-term tooth sensitivity after cold light whitening, especially those with pre-existing sensitive teeth. It is important for patients to communicate with their dentist before the treatment to determine if they are suitable candidates for this procedure.
7.3 Unstable Long-Term Results
While cold light whitening significantly improves the appearance of teeth, the whitening effect is not permanent. Patients will need to maintain proper oral hygiene and possibly undergo touch-up treatments to preserve the results.
VIII. Future Trends in Cold Light Teeth Whitening
As technology continues to evolve, cold light whitening techniques are also advancing. Future trends may include:
- Innovation in Materials and Technology: New whitening agents may be developed to provide longer-lasting and safer results. More advanced light technologies may also improve treatment efficiency and reduce discomfort.
- Personalized Treatment Plans: Future cold light whitening treatments may become more personalized, tailored to the individual’s unique tooth condition, discoloration type, and oral health.
- Painless Whitening Technology: Future advancements may focus on reducing or eliminating discomfort during the whitening process, making the treatment even more comfortable for patients.
IX. Conclusion
Cold light teeth whitening is an efficient, safe, and effective technique for improving the color of teeth. It offers a rapid solution to address extrinsic staining and mild intrinsic discoloration. Compared to traditional whitening methods, cold light whitening provides more noticeable and lasting results. Although the effects may not be permanent, the treatment can significantly enhance the patient’s smile and confidence. As technology progresses, cold light whitening is likely to become even more effective, safer, and accessible, benefiting a broader range of patients seeking to achieve a brighter, healthier smile.













































Discussion about this post