As the golden years unfold, our bodies undergo various transformations, and one area that often sees significant changes is our oral health. The elderly population faces a myriad of oral health concerns that can significantly impact their quality of life. From tooth decay and gum disease to oral cancer and dry mouth, understanding these issues and taking proactive steps can help maintain a healthier smile and overall well-being. This article delves into the most common oral health problems faced by seniors, their causes, and effective strategies for prevention and management.
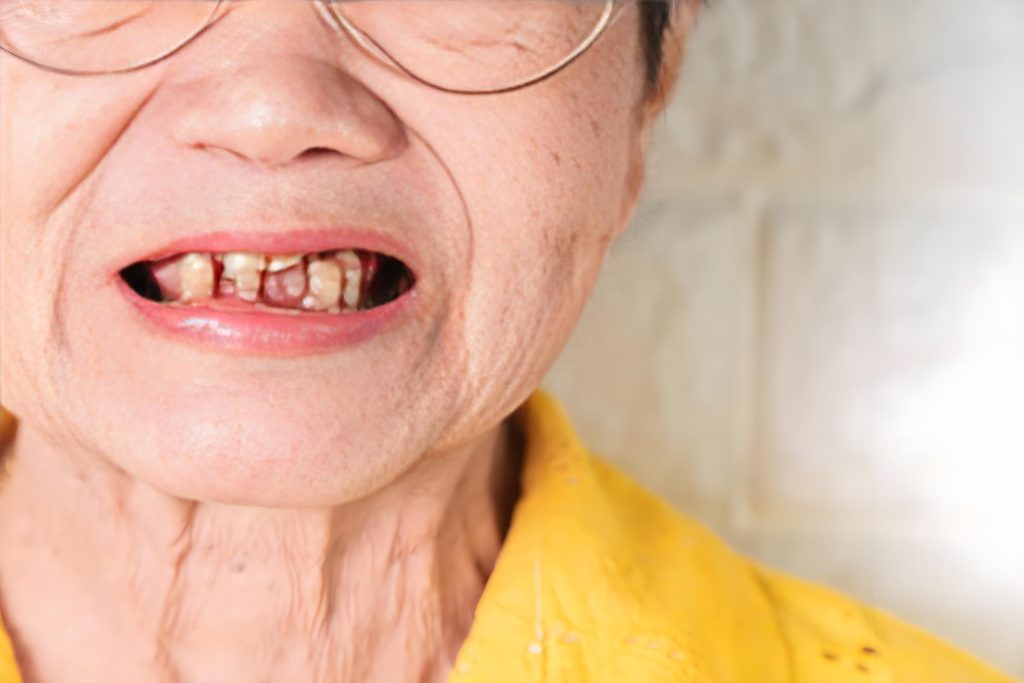
1. Tooth Decay: A Persistent Threat
Tooth decay, also known as dental caries, is a common oral health issue among the elderly. Age-related changes in saliva production and diet can contribute to a higher risk of decay. Saliva plays a crucial role in neutralizing acids produced by bacteria in the mouth, thereby protecting teeth from decay. However, as we age, our salivary glands may not produce as much saliva, leading to a dry mouth environment that is conducive to bacteria growth.
Causes:
- Dry mouth
- Poor oral hygiene practices
- Frequent consumption of sugary foods and drinks
- Use of certain medications
Prevention and Management:
- Maintain good oral hygiene by brushing teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste.
- Floss daily to remove plaque and food particles stuck between teeth.
- Use an alcohol-free mouthwash to keep the mouth moist and reduce bacteria.
- Increase water intake to stimulate saliva production.
- Avoid sugary snacks and drinks, especially sticky candies that can linger on teeth.
- Regular dental check-ups and cleanings are essential for early detection and treatment of decay.
2. Gum Disease: A Silent Invader
Gum disease, or periodontitis, is another prevalent oral health concern for the elderly. It is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects the gums and the bones supporting the teeth. Left untreated, gum disease can lead to tooth loss and systemic health issues such as heart disease and diabetes.
Causes:
- Poor oral hygiene
- Accumulation of plaque and tartar
- Smoking and tobacco use
- Systemic diseases like diabetes
- Certain medications that reduce saliva flow
Prevention and Management:
- Practice thorough daily oral hygiene, including brushing, flossing, and using an antiseptic mouthwash.
- Quit smoking and avoid tobacco products.
- Manage chronic conditions like diabetes to reduce the risk of gum disease.
- Visit the dentist regularly for professional cleanings and assessments.
- In cases of advanced gum disease, treatments such as scaling and root planing, or even surgical procedures, may be necessary.
3. Dry Mouth: A Parching Problem
Dry mouth, or xerostomia, is a common complaint among older adults. It occurs when the mouth doesn’t produce enough saliva to keep it moist. Saliva is vital for maintaining oral health as it washes away food particles, neutralizes acids, and protects teeth from decay.
Causes:
- Age-related changes in salivary gland function
- Use of certain medications (antihistamines, diuretics, antidepressants)
- Medical conditions like diabetes, Sjögren’s syndrome, and rheumatoid arthritis
- Mouth breathing
- Dehydration
Prevention and Management:
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day.
- Chew sugar-free gum or suck on sugar-free candies to stimulate saliva production.
- Use a humidifier at night to keep the air in your bedroom moist.
- Avoid caffeinated and alcoholic beverages, as they can dehydrate you further.
- Consult with your healthcare provider about adjusting medications that may cause dry mouth.
- Apply a moisturizing oral gel or spray if recommended by your dentist.
4. Oral Cancer: A Silent Danger
While not as common as other oral health issues, oral cancer poses a serious threat to the elderly population. Early detection is crucial for successful treatment and improved survival rates.
Causes:
- Smoking and tobacco use
- Heavy alcohol consumption
- Poor oral hygiene
- Chronic sun exposure to the lips
- Certain genetic predispositions and viral infections (HPV)
Prevention and Management:
- Avoid tobacco products and excessive alcohol consumption.
- Practice good oral hygiene to reduce inflammation and infection.
- Use sunscreen on your lips when exposed to the sun.
- Undergo regular oral cancer screenings during dental check-ups.
- Be aware of warning signs such as persistent mouth sores, red or white patches, difficulty swallowing, and changes in speech.
- Promptly report any suspicious symptoms to your healthcare provider.
5. Tooth Loss: An不可避免 Reality
Tooth loss is a common occurrence among the elderly, often resulting from long-term dental issues like gum disease, decay, or trauma. While tooth loss can significantly impact one’s ability to eat, speak, and smile confidently, modern dentistry offers several solutions to restore oral function and aesthetics.
Causes:
- Advanced gum disease
- Severe tooth decay
- Trauma or accidents
- Wear and tear from grinding or clenching teeth
Prevention and Management:
- Maintain good oral hygiene to prevent gum disease and decay.
- Wear a mouthguard during sports to protect teeth from trauma.
- Seek prompt dental treatment for any signs of infection or decay.
- In cases of tooth loss, consider dental implants, bridges, or dentures to restore function and aesthetics.
- Regular dental check-ups can help identify and address potential problems before they lead to tooth loss.
Conclusion: Embracing a Healthier Smile in the Golden Years
Navigating the oral health challenges of aging requires a proactive approach that combines daily hygiene practices, regular dental visits, and an understanding of the unique needs of senior oral health. By addressing common issues like tooth decay, gum disease, dry mouth, oral cancer, and tooth loss, older adults can maintain a healthier smile and enjoy a better quality of life. Remember, oral health is a vital component of overall well-being, and with the right care, it’s possible to keep your smile bright and your mouth healthy as you age gracefully.













































Discussion about this post