Introduction: The Evolution of Dentistry
Over the years, dentistry has evolved significantly, largely due to technological advancements. One of the most exciting innovations in the field of dental care is the emergence of digital dentistry. While traditional methods have served patients well for centuries, digital dentistry has introduced new possibilities, offering higher precision, improved patient comfort, and faster results.
But what exactly differentiates digital dentistry from traditional dentistry? How do these two approaches compare in terms of treatment outcomes, time efficiency, and cost? And most importantly, how can you, as a patient, decide which treatment method is best for your oral health needs?
In this article, we will explore both digital and traditional dentistry in depth, examining their differences, benefits, drawbacks, and how these innovations can enhance your dental care. We will also guide you on how to make an informed decision about the treatment plan that best suits your situation.
1. Traditional Dentistry: A Time-Tested Approach
1.1 Overview of Traditional Dentistry
Traditional dentistry refers to the conventional methods and tools used in dental practice that have been in use for decades or even centuries. These techniques and tools have evolved over time but continue to form the foundation of modern dental care.
Key Characteristics of Traditional Dentistry:
- Manual impressions for crowns, bridges, dentures, and other restorations.
- Use of X-rays for diagnosis and treatment planning.
- Standard dental tools, such as hand instruments for cleanings, fillings, and extractions.
- Local anesthetics and manual methods to control pain and discomfort.
1.2 The Process in Traditional Dentistry
In a traditional dental treatment, the process usually begins with an initial consultation and diagnostic X-rays. The dentist then physically examines the patient’s teeth and gums, identifies any problems, and creates a treatment plan. For restorative treatments like crowns or bridges, manual impressions are taken by using a soft, moldable material that captures the shape of the teeth. These impressions are then sent to a dental lab, where custom restorations are made by hand.
Examples of Treatments in Traditional Dentistry:
- Fillings for cavities
- Crowns and bridges
- Root canal treatments
- Dentures
- Tooth extractions
1.3 Advantages of Traditional Dentistry
- Familiarity: Traditional methods have been around for decades, and most dentists are highly skilled in using these techniques.
- Well-Established: The processes and equipment used in traditional dentistry have undergone years of testing and refinement, making them trusted solutions for many dental issues.
- Comprehensive: Traditional dentistry is versatile and can address a wide range of dental needs.
1.4 Drawbacks of Traditional Dentistry
- Time-Consuming: The process of taking impressions, creating restorations, and fitting them can be lengthy and require multiple appointments.
- Inaccuracy: Manual impressions can sometimes lead to imperfections that may result in poorly fitting restorations.
- Discomfort: Some patients find traditional impressions to be uncomfortable, as they can trigger a gag reflex.
2. Digital Dentistry: The Modern Revolution in Oral Care
2.1 What Is Digital Dentistry?
Digital dentistry refers to the use of digital technology to assist in the diagnosis, planning, and execution of dental treatments. This includes computer-aided design (CAD), 3D imaging, laser scanning, and other high-tech tools that enhance the speed, precision, and overall effectiveness of dental procedures.
Key Technologies in Digital Dentistry:
- CAD/CAM (Computer-Aided Design and Computer-Aided Manufacturing): Allows for the creation of restorations, such as crowns and bridges, directly in the office using digital scanning and 3D printing.
- 3D Digital Imaging: Provides more detailed and accurate images of the teeth and soft tissues, leading to better treatment planning.
- Intraoral Scanners: Replace traditional impression materials with high-precision digital scans of the teeth and gums.
- Digital X-rays: Provide clear, high-resolution images with lower radiation exposure compared to traditional X-rays.
2.2 How Digital Dentistry Works
In digital dentistry, the treatment process often starts with the use of intraoral scanners to capture 3D images of the teeth and mouth. This process replaces the uncomfortable manual impression process, offering a more comfortable and faster alternative. Once the digital impression is captured, it is used to design restorations in a computer program (CAD). These designs can then be directly transferred to a milling machine (CAM), which creates the restoration in the office, often in a single appointment.
Examples of Treatments in Digital Dentistry:
- Same-day crowns and bridges using CAD/CAM technology
- Clear aligners and orthodontic treatment planning
- 3D digital X-rays for accurate diagnosis
- Laser treatments for gum contouring or cavity detection
2.3 Advantages of Digital Dentistry
- Accuracy: Digital scans are highly accurate, reducing the risk of misfits in restorations like crowns and bridges.
- Efficiency: Many digital dental treatments can be completed in a single appointment, saving time for both the dentist and patient.
- Comfort: Intraoral scanners are far more comfortable than traditional impressions, eliminating gagging and discomfort.
- Better Visualization: With 3D imaging, dentists can view teeth and soft tissues in more detail, leading to better diagnoses and treatment plans.
- Reduced Radiation Exposure: Digital X-rays expose patients to significantly less radiation than traditional film X-rays.
2.4 Drawbacks of Digital Dentistry
- Cost: The initial setup cost for digital dental equipment can be high, which may reflect in the cost of treatments.
- Learning Curve: While digital dentistry is more efficient, it requires advanced training, and not all dental offices may have the technology or expertise to use it.
- Availability: Some dental practices, especially smaller ones, may not have the necessary digital tools or resources to offer these treatments.
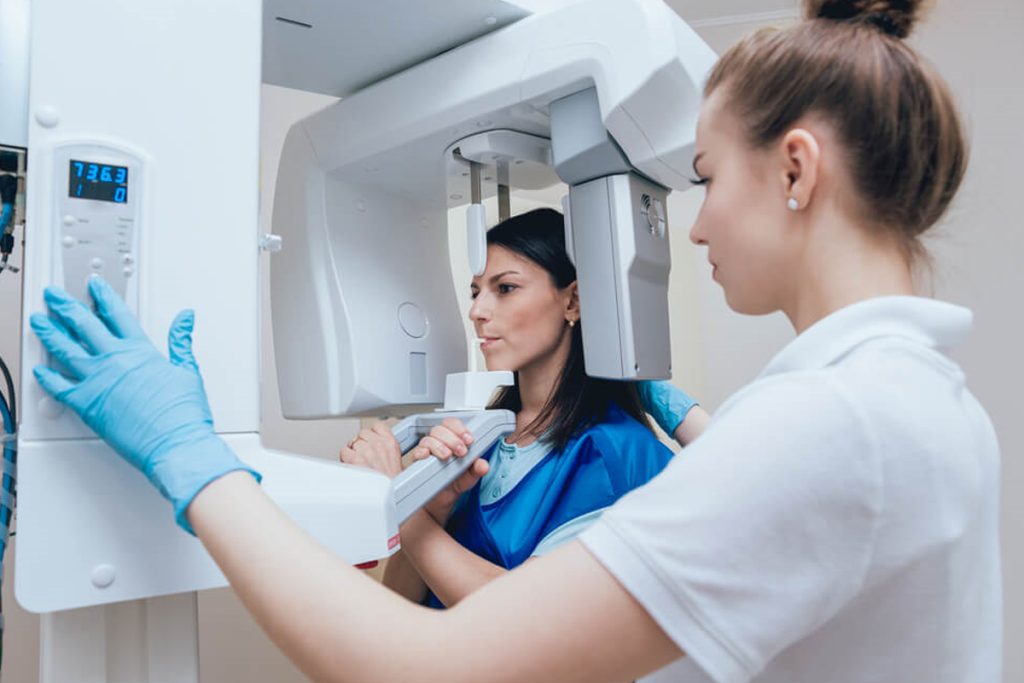
3. Key Differences Between Digital and Traditional Dentistry
3.1 Treatment Time
- Traditional Dentistry: Multiple appointments are often required, especially for procedures such as crowns, bridges, or dentures, as impressions need to be sent to a lab.
- Digital Dentistry: Many treatments, such as crowns and fillings, can be completed in a single appointment, thanks to in-office CAD/CAM systems.
3.2 Precision and Accuracy
- Traditional Dentistry: Manual impressions may lead to slight inaccuracies, affecting the fit of restorations and requiring adjustments.
- Digital Dentistry: Digital scans provide a much higher level of precision, ensuring better-fitting restorations and more accurate treatment planning.
3.3 Comfort and Convenience
- Traditional Dentistry: Impressions taken with traditional materials can be uncomfortable, especially for patients with sensitive gag reflexes.
- Digital Dentistry: Intraoral scans are less invasive and more comfortable, offering a significant improvement in patient experience.
3.4 Cost
- Traditional Dentistry: Traditional techniques are generally more affordable due to lower equipment costs, although this can vary depending on the procedure.
- Digital Dentistry: The initial cost of digital equipment can be high, potentially making treatments more expensive, though the long-term benefits and time savings can justify the price.
4. How to Choose the Best Treatment for You
Choosing between traditional and digital dentistry largely depends on several factors, including the type of treatment required, personal preferences, the availability of technology in your dental practice, and cost considerations.
4.1 Consider Your Specific Treatment Needs
Some treatments, like simple fillings or extractions, may be equally effective with both traditional and digital approaches. However, more complex procedures like crowns, bridges, and dentures often benefit from digital techniques due to their precision and efficiency.
4.2 Ask About Technology Availability
Before making a decision, inquire about the technologies available at your dental office. While some dentists have fully embraced digital tools, others may still rely heavily on traditional methods. Make sure you understand the pros and cons of the available treatment options.
4.3 Understand Cost Implications
Digital dentistry may involve higher upfront costs, but it can offer long-term benefits like fewer visits, quicker recovery, and better precision. Consider your budget and whether the added convenience of digital tools is worth the investment for your treatment.
4.4 Consult with Your Dentist
Your dentist can help you make an informed decision by providing recommendations based on your specific oral health needs. They will consider the best treatment plan for your case, factoring in your health, the complexity of the procedure, and available technologies.
5. Conclusion: Embracing the Future of Dentistry
Both digital and traditional dentistry have their place in modern oral care, with each offering unique benefits. Digital dentistry, with its precision, efficiency, and patient comfort, is rapidly gaining popularity, especially for more complex and restorative treatments. However, traditional methods still remain effective and are often more accessible for straightforward procedures.
Ultimately, the choice between digital and traditional dentistry comes down to your specific needs, budget, and the technology available at your dentist’s practice. By understanding the differences and advantages of each, you can make an informed decision that ensures the best possible treatment for your dental health.












































Discussion about this post